Introduction
Monitoring isn’t just a job; it’s a crucial part of managing systems. It helps you understand how your system is performing, find problems, and make it work better. This article shows you how to set up a strong monitoring system using Prometheus, Grafana, and node_exporter, all managed with Docker Compose. We’ll explain why each setting is important, not just how to do it
Prerequisites
Docker and Docker Compose: Ensure Docker and Docker Compose are installed on your server.
Setup Prometheus
- Create a docker-compose.yml file with the following content.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
version: '3.8' # Docker Compose version
networks: # Define networks for the services
monitoring: # Name of the network
driver: bridge # Use the bridge driver
volumes:
prometheus_data: {} # Prometheus data volume
services:
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
container_name: prometheus
restart: unless-stopped
volumes: # Mount volumes for configuration and data
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml # Mount the Prometheus configuration file
- prometheus_data:/prometheus # Mount the Prometheus data volume
command:
- '--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml' # Path to the configuration file
- '--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus' # Path to store the time-series database data
- '--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries' # Path to console libraries
- '--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles' # Path to console templates
- '--web.enable-lifecycle' # Enable lifecycle
expose: # Expose ports from the container
- 9090 # Prometheus web UI port
ports: # Map ports from the container to the host
- "30150:9090" # Map container port 9090 to host port 30150
networks: # Attach the service to the monitoring network
- monitoring
|
- Create a prometheus.yml file in the same directory with your Prometheus configuration.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
global: # Global configuration settings for Prometheus
scrape_interval: 30s # How often to scrape targets (30 seconds in this case)
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 30s # How often to scrape this job (30 seconds in this case)
static_configs: # Define static targets to scrape
- targets: ['localhost:9090'] # The target to scrape (Prometheus itself in this case, running on localhost:9090)
|
-
Run docker-compose up -d to start Prometheus in the background.
-
Go to your serverip:30150/targets to check the services.
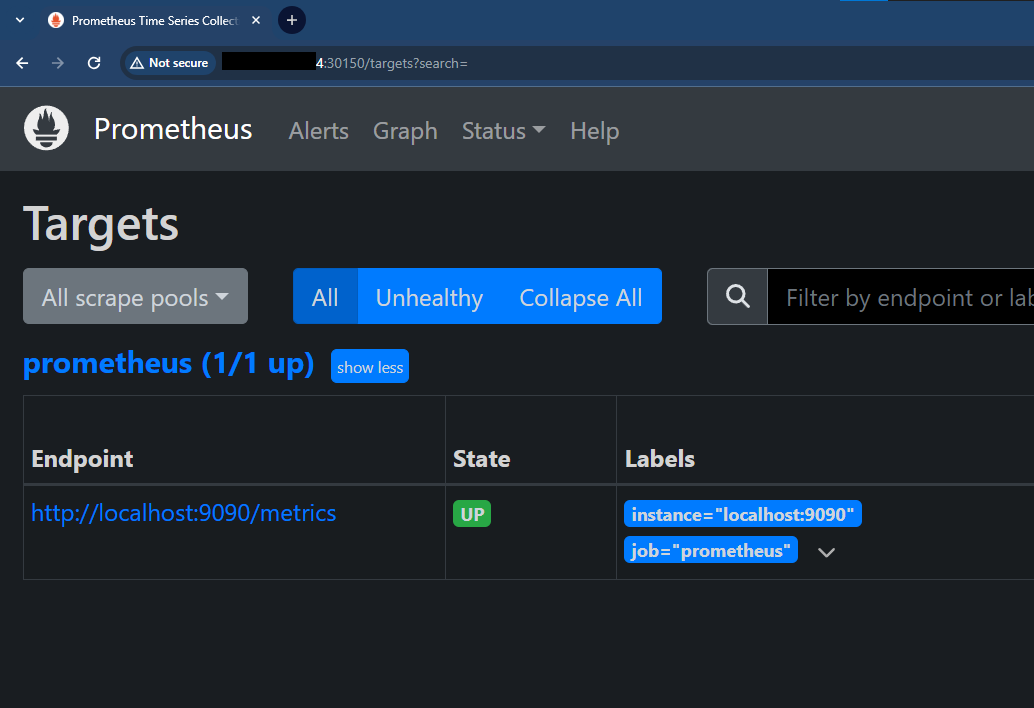
Setup Grafana
- Add the following service to your existing docker-compose.yml file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: grafana
ports:
- 30160:3000 # Map container port 3000 to host port 30160
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER=admin # Set the admin user for Grafana
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=grafana # Set the admin password for Grafana
volumes: # Mount volumes for Grafana configuration
- ./grafana:/etc/grafana/provisioning/datasources # Mount the Grafana configuration directory
networks: # Attach the service to the monitoring network
- monitoring
|
-
Run docker-compose up -d to start Grafana in the background.
-
Go to your serverip:30160 to check the services.
Node Exporter
- Add the following service to your existing docker-compose.yml file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
node-exporter:
image: prom/node-exporter:latest
container_name: node-exporter
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /proc:/host/proc:ro # Mount the proc directory from the host
- /sys:/host/sys:ro # Mount the sys directory from the host
- /:/rootfs:ro # Mount the root filesystem from the host
command:
- '--path.procfs=/host/proc' # Path to the procfs directory
- '--path.rootfs=/rootfs' # Path to the root filesystem
- '--path.sysfs=/host/sys' # Path to the sysfs directory
- '--collector.filesystem.mount-points-exclude=^/(sys|proc|dev|host|etc)($$|/)' # Exclude certain filesystem mount points from collection
expose:
- 9100 # Expose ports from the container
networks: # Attach the service to the monitoring network
- monitoring
|
- Run
docker-compose up -d to start Node Exporter in the background.
This setup will deploy Prometheus, Grafana, and Node Exporter containers, allowing you to monitor your environment easily.
Configurate Grafana Dashboard
-
Go to the Grafana URL provided in the Grafana setup step and log in using the credentials found in the docker-compose file.
-
Once logged in, navigate from the sidebar to Configuration -> Data Sources -> Add new Data Source.
Search for Prometheus and select it. Fill in the following information:
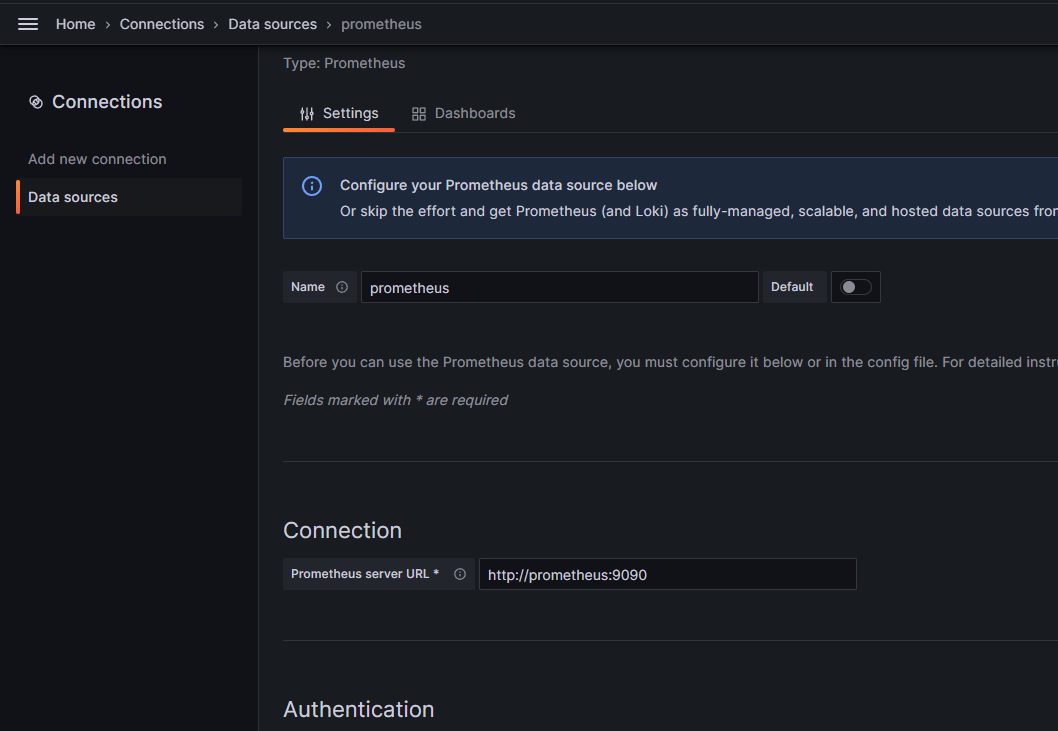
-
Scroll down and click Save & Test. This will test the connection to your Prometheus server.
You now have a data source configured for your system data in Grafana.
-
Go to the Dashboard section and create a new dashboard. Click on Import Dashboard.
-
Enter the ID of the dashboard you want to import. Since we are using the “Node Exporter Full” dashboard from Grafana, enter the ID “1860” and click Load.
-
Now you’ll see the amazing insights and visualizations provided by the “Node Exporter Full” dashboard in Grafana, giving you a comprehensive view of your system’s metrics.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have successfully set up a robust monitoring stack using Prometheus, Grafana, and node_exporter, orchestrated through Docker Compose. We configured Prometheus to scrape metrics from our system and Grafana to visualize these metrics in a dashboard. By following these steps, you now have a powerful monitoring solution for understanding the performance of your system, detecting anomalies, and optimizing resources. Monitoring is not just a task; it’s an essential part of system administration that helps you keep your systems running smoothly.



